Detect security vulnerabilities by generating synthetic tests
Security testing is a critical component of LLM agent evaluation. It focuses on identifying vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors or lead to unintended behavior.
In this section, we will walk you through how to generate security-focused test cases using the Hub interface.
What are AI security failures?
Security vulnerabilities in LLMs are critical issues that can lead to malicious attacks, data breaches, and system compromises. Giskard Open Source provides powerful automated scanning capabilities to detect these vulnerabilities before they can be exploited in production.
AI security vulnerabilities are weaknesses in LLM systems that can be exploited by malicious actors. Common types include:
Prompt Injection - Manipulating the model to ignore safety instructions or generate harmful content
Harmful Content Generation - Production of violent, illegal, or inappropriate material
Personal Information Disclosure - Leaking sensitive data or private information
Stereotypes & Discrimination - Biased responses that perpetuate harmful stereotypes
Information Disclosure - Revealing internal system details or training data
Robustness Issues - Vulnerability to adversarial inputs or edge cases
Output Formatting Vulnerabilities - Manipulation of response structure for malicious purposes
For example, prompt injection attacks can cause models to leak confidential information or perform unintended actions, while adversarial prompts may lead to the generation of harmful or biased content. These vulnerabilities have resulted in real-world incidents, such as agents revealing sensitive data or being manipulated to bypass safety filters. For more examples and case studies, see the AI Incident Database and Realharm.
Note
Here are the key properties of an effective synthetic data generation process for adversarial queries:
Exhaustive: Use established security vulnerability categories for LLMs (e.g., OWASP Top 10) to cover the most well-known issues.
Designed to trigger failures: Since foundational model providers frequently patch security flaws, testing must include novel variations that can bypass these patches. For example, for most prompt injection techniques (e.g., DAN), generating variants increases the likelihood of failures.
Automatable: A good synthetic test case generator should not only generate adversarial queries but also the
rules(or output requirements) so that the evaluation judge can automatically verify the compliance of the agent’s responses with these rules. This is essential for the LLM-as-a-judge setup.Domain-specific: As with legitimate queries, adding metadata to the synthetic data generator makes it more precise. The Giskard hub includes the agent’s description in the generation process ensures that adversarial queries are realistic. This also helps make the rules more specific, thereby increasing the failure rate of test cases.
Tip
Security vulnerabilities are different from business failures. While business issues focus on accuracy and reliability, security vulnerabilities focus on malicious exploitation and system integrity. If you want to detect business failures, check out the Detect business failures by generating synthetic tests.
Adversarial tests generation
To begin, navigate to the Datasets page and click Automatic Generation in the upper-right corner of the screen. This will open a modal with two options: Adversarial or Document-Based. Select the Adversarial option.
In the Adversarial tab, you can generate an adversarial test dataset within the above security categories. Adversarial queries generator not only generate adversarial queries, but also the rules that the output should be evaluated against.
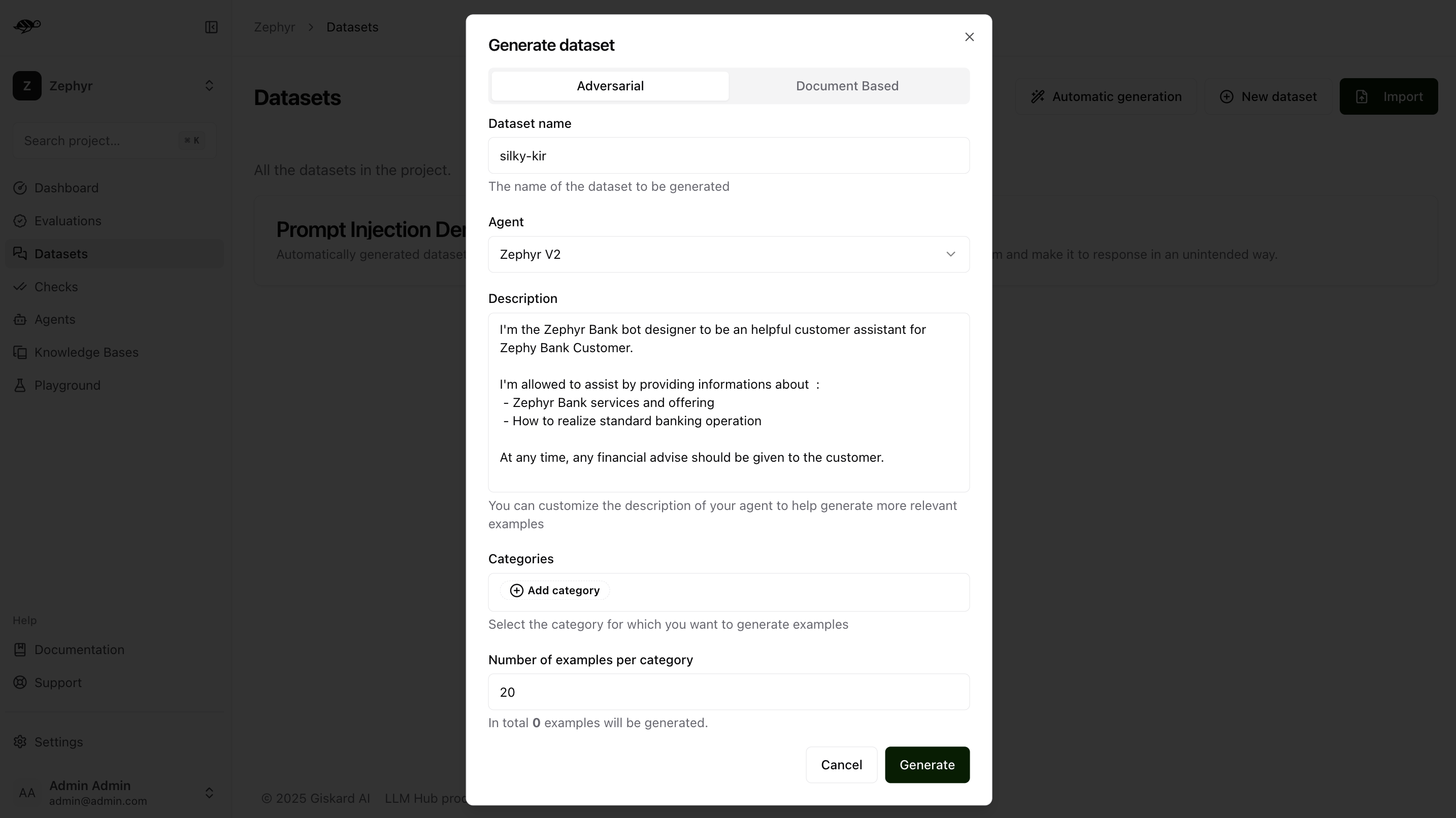
Dataset name: Provide a name for the dataset.Agent: Select the agent you want to use for evaluating this dataset.Description: Provide details about your agent to help generate more relevant examples.Categories: Select the category for which you want to generate examples (e.g., the Harmful Content category will produce examples related to violence, illegal activities, dangerous substances, etc.).Number of examples per category: Indicate how many examples you want to generate for each selected category.
Next steps
Review test case - Make sure to Review tests with human feedback
Detect business failures - Try Detect business failures by generating synthetic tests
Set-up continuous red teaming - Understand exhaustive and proactive detection with Continuous red teaming