Evaluate local models¶
In the Run evaluations section we have seen how to run evaluations against models for which you have an API endpoint. However, during the development phase, you may want to evaluate a local model that is not yet exposed with an API.
This is the topic of this section. We will show how to run evaluations against local models using the Hub. In this way, the evaluations will still be performed and stored in the Hub (and you can use datasets from the Hub), but the model will be run locally.
Running the evaluation will allow you to compare the performance of your local model with the one that is already in production, or with other models that you use as a baseline. You will also be able to debug performance issues by checking each conversation in the Hub inteface.
Hint
You may also want to use this method in your CI/CD pipeline, to perform checks when the code or the prompts of your agent get updated.
Let’s initialize the Hub client and the project we will be working with:
import os
from giskard_hub import HubClient
hub = HubClient()
project_id = os.getenv("HUB_PROJECT_ID")
Preparing the model¶
To execute a local model, you just need to define a Python function. This function should take a list of messages and return an output message.
Here is an example of a simple model that just echoes the last user message:
from typing import List
from giskard_hub.data import ChatMessage
def my_local_bot(messages: List[ChatMessage]) -> str:
"""A simple bot that echoes the last user message."""
msg = messages[-1].content
return f"You said: '{msg}'"
There are a few things to note here:
The function takes a list of
ChatMessageobjects as input. This object has two fields: role (e.g. “user” or “assistant”) and content (the message content).The function should return a string or an instance of
ModelOutput(if you want more control)Include a docstring that describes what the model does. This is equivalent to the description of the model in the Hub and will be used to improve the reliability of evaluations.
The name of the function (e.g.
my_local_bot) will be used as the model name when showing the evaluation run in the Hub.
You can check that everything works simply by running the function:
my_local_bot([ChatMessage(role="user", content="Hello")])
# Output: "You said: 'Hello'"
Run the evaluation¶
Running the evaluation is similar to what we have seen for remove evaluations
(see Run evaluations). Instead of passing a remote model ID to the
evaluate method of the Hub client, we will pass the function we defined
above.
Let’s select the dataset we want to use for the evaluation.
dataset_id = os.getenv("HUB_EVAL_DATASET_ID") # or directly set the ID
We can now launch the evaluation run:
eval_run = hub.evaluate(
model=my_local_bot,
dataset=dataset_id,
# optionally, specify a name
name="test-run",
)
The evaluation run will be queued and processed by the Hub. As usual, wait for the evaluation run to complete and then print the results:
# This will block until the evaluation is completed
eval_run.wait_for_completion()
# Print the metrics
eval_run.print_metrics()
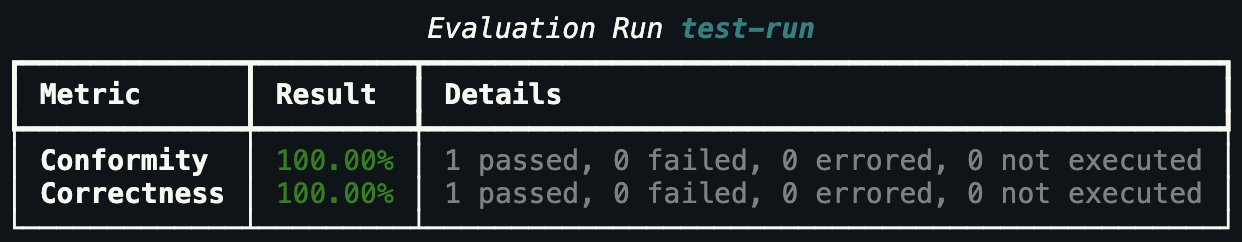
Evaluation metrics output¶
You can also check the results in the Hub interface and compare it with other evaluation runs.